Portal:Sex work
Introduction

Sex work is "the exchange of sexual services, performances, or products for material compensation. It includes activities of direct physical contact between buyers and sellers as well as indirect sexual stimulation". Sex work only refers to voluntary sexual transactions; thus, the term does not refer to human trafficking and other coerced or nonconsensual sexual transactions such as child prostitution. The transaction must take place between consenting adults of the legal age and mental capacity to consent and must take place without any methods of coercion, other than payment. The term emphasizes the labor and economic implications of this type of work. Furthermore, some prefer the use of the term because it grants more agency to the sellers of these services. (Full article...)
Selected article -
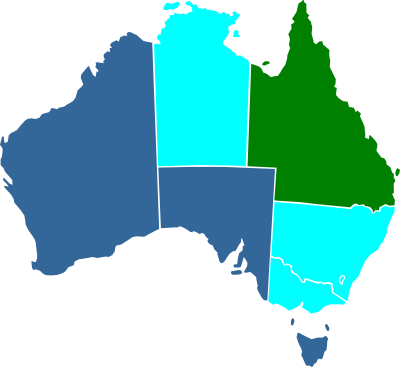
Prostitution in Australia is governed by state and territory laws, which vary considerably, although none ban prostitution outright.
- Tasmania, Western Australia and South Australia operate under an abolitionism framework, where the selling of sex itself is not illegal, but activities such as keeping brothels and pimping are illegal.
- Queensland operates under a legalization framework, where sex work is legal, but brothels must be licensed and can face criminal penalties for operating without a license. Private sex work is legal if the sex worker is working alone. A bill was introduced into the Parliament of Queensland on 15 February 2024 to decriminalise most criminal penalties relating to sex work, such as the requirement for brothels to be licensed or for sex workers outside of licensed brothels to have to work alone.
- The Northern Territory, New South Wales, the Australian Capital Territory and Victoria operate under a decriminalisation framework, where most criminal penalties associated with sex work have been removed and brothels or prostitutes are not required to be licensed, however all jurisdictions still have some remaining regulations in regards to where prostitutes or brothels can operate, or on other activities such as advertising.
Selected images
Related portals
Selected general sex worker
Did you know...
- ... that Lea Ackermann, a German nun of the Missionary Sisters of Our Lady of Africa, fought against forced prostitution and sex tourism in East Africa?
- ... that the posthumously released documentary Clean centered on the life of Sandra Pankhurst, a former sex worker, drag queen, and crime scene cleaner?
- ... that a Harvey's franchise known for being a hub for sex work was described by one artist as a "legendary Toronto icon"?
Subcategories
Get involved

For editor resources and to collaborate with other editors on improving Wikipedia's Sex work-related articles, see WikiProject Sex work.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus




























































